30 KiB
Swayr & Swayrbar
Table of Contents
Swayr, a window-switcher & more for sway
Swayr consists of a demon, and a client. The demon swayrd records
window/workspace creations, deletions, and focus changes using sway's JSON IPC
interface. The client swayr offers subcommands, see swayr --help, and
sends them to the demon which executes them.
Swayr commands
The swayr binary provides many subcommands of different categories.
Non-menu switchers
Those are just commands that toggle between windows without spawning the menu program.
switch-to-urgent-or-lru-windowswitches to the next window with urgency hint (if any) or to the last recently used window.switch-to-app-or-urgent-or-lru-windowswitches to a specific window matched by application ID or window class unless it's already focused. In that case, it acts just likeswitch-to-urgent-or-lru-window. For example, you can provide "firefox" as argument to this command to have a convenient firefox <-> last-recently-used window toggle.switch-to-mark-or-urgent-or-lru-windowswitches to a specific window matched by mark (con_mark) unless it's already focused. In that case, it acts just likeswitch-to-urgent-or-lru-window. For example, you can assign a "browser" mark to your browser window (using a standard swayfor_windowrule). Then you can provide "browser" as argument to this command to have a convenient browser <-> last-recently-used window toggle.
Menu switchers
Those spawn a menu program where you can select a window (or workspace, or output, etc.) and act on that.
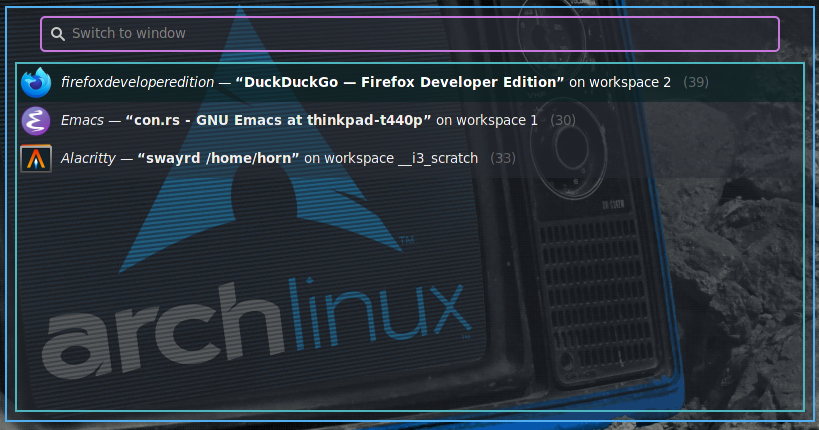
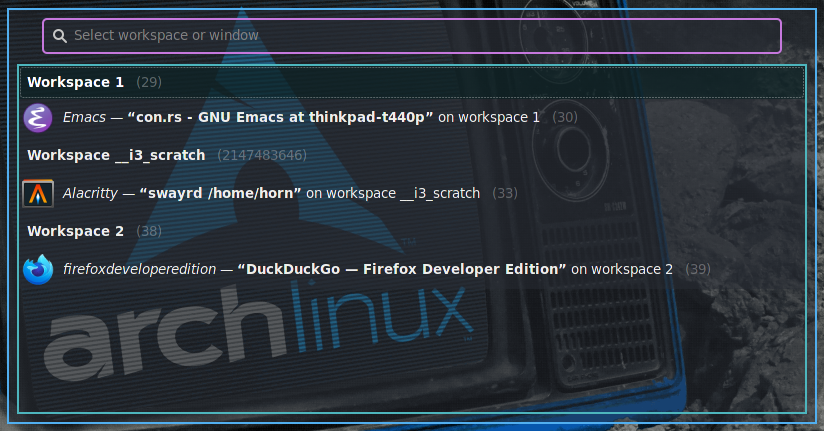
switch-windowdisplays all windows in the order urgent first, then last-recently-used, focused last and focuses the selected.switch-workspacedisplays all workspaces in LRU order and switches to the selected one.switch-outputshows all outputs in the menu and focuses the selected one.switch-workspace-or-windowdisplays all workspaces and their windows and switches to the selected workspace or window.switch-workspace-container-or-windowshows workspaces, containers, and their windows in the menu program and switches to the selected one.switch-toshows outputs, workspaces, containers, and their windows in the menu program and switches to the selected one.quit-windowdisplays all windows and quits the selected one. An optional--kill/-kflag may be specified in which case the window's process will be killed usingkill -9 <pid>rather than only sending akillIPC message to sway.quit-workspace-or-windowdisplays all workspaces and their windows and allows to quit either the selected workspace (all its windows) or the selected window.quit-workspace-container-or-windowshows workspaces, containers, and their windows and quits all windows of the selected workspace/container or the selected window.move-focused-to-workspacemoves the currently focused window or container to another workspace selected with the menu program. Non-matching input of the form#w:<workspace>where the hash andw:shortcut are optional can be used to move it to a new workspace.move-focused-tomoves the currently focused container or window to the selected output, workspace, container, window. Non-matching input is handled like withmove-focused-to-workspace.swap-focused-withswaps the currently focused window or container with the one selected from the menu program.
Menu shortcuts for non-matching input
All menu switching commands (switch-window, switch-workspace, and
switch-workspace-or-window) now handle non-matching input instead of doing
nothing. The input should start with any number of # (in order to be able to
force a non-match), a shortcut followed by a colon, and some string as required
by the shortcut. The following shortcuts are supported.
w:<workspace>: Switches to a possibly non-existing workspace.<workspace>must be a digit, a name or<digit>:<name>. The<digit>:<name>format is explained inman 5 sway. If that format is given,swayrwill create the workspace usingworkspace number <digit>:<name>. If just a digit or name is given, thenumberargument is not used.s:<cmd>: Executes the sway command<cmd>usingswaymsg.- Any other input is assumed to be a workspace name and thus handled as
w:<input>would do.
Cycling commands
Those commands cycle through (a subset of windows) in last-recently-used order.
next-window (all-workspaces|current-workspace)&prev-window (all-workspaces|current-workspace)focus the next/previous window in depth-first iteration order of the tree. The argumentall-workspacesorcurrent-workspacedefine if all windows of all workspaces or only those of the current workspace are considered.next-tiled-window&prev-tiled-windowdo the same asnext-window&prev-windowbut switch only between windows contained in a tiled container.next-tabbed-or-stacked-window&prev-tabbed-or-stacked-windowdo the same asnext-window&prev-windowbut switch only between windows contained in a tabbed or stacked container.next-floating-window&prev-floating-windowdo the same asnext-window&prev-windowbut switch only between floating windows.next-window-of-same-layout&prev-window-of-same-layoutis likenext-floating-window/prev-floating-windowif the current window is floating, it is likenext-tabbed-or-stacked-window/prev-tabbed-or-stacked-windowif the current window is in a tabbed or stacked container, it is likenext-tiled-window/prev-tiled-windowif the current windows is in a tiled container, and is likenext-window/prev-windowotherwise.
Layout modification commands
These commands change the layout of the current workspace.
tile-workspace exclude-floating|include-floatingtiles all windows on the current workspace (excluding or including floating ones). That's done by moving all windows away to some special workspace, setting the current workspace tosplithlayout, and then moving the windows back. If theauto_tilefeature is used, see the Configuration section below, it'll change from splitting horizontally to vertically during re-insertion.shuffle-tile-workspace exclude-floating|include-floatingshuffles & tiles all windows on the current workspace. The shuffle part means that (a) the windows are shuffled before re-insertion, and (b) a randomly chosen already re-inserted window is focused before re-inserting another window. So whiletile-workspaceon a typical horizontally oriented screen and 5 windows will usually result in a layout with one window on the left and all four others tiled vertially on the right,shuffle-tile-workspacein combination withauto_tileusually results in a more balanced layout, i.e., 2 windows tiled vertically on the right and the other 4 tiled vertially on the left. If you have less than a handful of windows, just repeatshuffle-tile-workspacea few times until happenstance creates the layout you wanted.tab-workspace exclude-floating|include-floatingputs all windows of the current workspace into a tabbed container.toggle-tab-shuffle-tile-workspace exclude-floating|include-floatingtoggles between a tabbed and tiled layout, i.e., it callsshuffle-tile-workspaceif it is currently tabbed, and callsshuffle-tile-workspaceif it is currently tiled.
Miscellaneous commands
configure-outputslets you repeatedly issue output configuration commands until you abort the menu program.execute-swaymsg-commanddisplays most swaymsg which don't require additional input and executes the selected one. That's handy especially for less often used commands not bound to a key. Non-matching input will be executed executed as-is withswaymsg.execute-swayr-commanddisplays all commands above and executes the selected one. (This is useful for accessing swayr commands which are not bound to a key.)
Screenshots
Installation
Some distros have packaged swayr so that you can install it using your distro's
package manager. Alternatively, it's easy to build and install it yourself
using cargo.
Distro packages
The following GNU/Linux and BSD distros package swayr. Thanks a lot to the respective package maintainers! Refer to the repology site for details.
Building with cargo
You'll need to install the current stable rust toolchain using the one-liner shown at the official rust installation page.
Then you can install swayr like so:
cargo install swayr
For getting updates easily, I recommend the cargo install-update plugin.
# Install it once.
cargo install install-update
# Then you can update all installed rust binary crates including swayr using:
cargo install-update --all
# If you only want to update swayr, you can do so using:
cargo install-update -- swayr
Usage
You need to start the swayr demon swayrd in your sway config
(~/.config/sway/config) like so:
exec env RUST_BACKTRACE=1 RUST_LOG=swayr=debug swayrd > /tmp/swayrd.log 2>&1
The setting of RUST_BACKTRACE=1, RUST_LOG=swayr=debug and the redirection
of the output to some logfile is optional but helps a lot when something
doesn't work. Especially, if you encounter a crash in certain situations and
you want to report a bug, it would be utmost helpful if you could reproduce the
issue with backtrace and logging at the debug level and attach that to your
bug report. Valid log levels in the order from logging more to logging less
are: trace, debug, info, warn, error, off.
Next to starting the demon, you want to bind swayr commands to some keys like so:
bindsym $mod+Space exec env RUST_BACKTRACE=1 \
swayr switch-window >> /tmp/swayr.log 2>&1
bindsym $mod+Delete exec env RUST_BACKTRACE=1 \
swayr quit-window >> /tmp/swayr.log 2>&1
bindsym $mod+Tab exec env RUST_BACKTRACE=1 \
swayr switch-to-urgent-or-lru-window >> /tmp/swayr.log 2>&1
bindsym $mod+Next exec env RUST_BACKTRACE=1 \
swayr next-window all-workspaces >> /tmp/swayr.log 2>&2
bindsym $mod+Prior exec env RUST_BACKTRACE=1 \
swayr prev-window all-workspaces >> /tmp/swayr.log 2>&2
bindsym $mod+Shift+Space exec env RUST_BACKTRACE=1 \
swayr switch-workspace-or-window >> /tmp/swayr.log 2>&1
bindsym $mod+c exec env RUST_BACKTRACE=1 \
swayr execute-swaymsg-command >> /tmp/swayr.log 2>&1
bindsym $mod+Shift+c exec env RUST_BACKTRACE=1 \
swayr execute-swayr-command >> /tmp/swayr.log 2>&1
Of course, configure the keys to your liking. Again, enabling rust backtraces and logging are optional.
Configuration
Swayr can be configured using the ~/.config/swayr/config.toml or
/etc/xdg/swayr/config.toml config file.
If no config files exists, a simple default configuration will be created on the first invocation for use with the wofi menu program.
It should be easy to adapt that default config for usage with other menu programs such as dmenu, bemenu, rofi, a script spawning a terminal with fzf, or whatever. The only requirement is that the launcher needs to be able to read the items to choose from from stdin and spit out the selected item to stdout.
The default config looks like this:
[menu]
executable = 'wofi'
args = [
'--show=dmenu',
'--allow-markup',
'--allow-images',
'--insensitive',
'--cache-file=/dev/null',
'--parse-search',
'--height=40%',
'--prompt={prompt}',
]
[format]
output_format = '{indent}<b>Output {name}</b> <span alpha=\"20000\">({id})</span>'
workspace_format = '{indent}<b>Workspace {name} [{layout}]</b> <span alpha="20000">({id})</span>'
container_format = '{indent}<b>Container [{layout}]</b> on workspace {workspace_name} <i>{marks}</i> <span alpha="20000">({id})</span>'
window_format = 'img:{app_icon}:text:{indent}<i>{app_name}</i> — {urgency_start}<b>“{title}”</b>{urgency_end} on workspace {workspace_name} <i>{marks}</i> <span alpha="20000">({id})</span>'
indent = ' '
urgency_start = '<span background="darkred" foreground="yellow">'
urgency_end = '</span>'
html_escape = true
icon_dirs = [
'/usr/share/icons/hicolor/scalable/apps',
'/usr/share/icons/hicolor/64x64/apps',
'/usr/share/icons/hicolor/48x48/apps',
'/usr/share/icons/Adwaita/64x64/apps',
'/usr/share/icons/Adwaita/48x48/apps',
'/usr/share/pixmaps',
]
[layout]
auto_tile = false
auto_tile_min_window_width_per_output_width = [
[1024, 500],
[1280, 600],
[1400, 680],
[1440, 700],
[1600, 780],
[1920, 920],
[2560, 1000],
[3440, 1000],
[4096, 1200],
]
In the following, all sections are explained.
The menu section
In the [menu] section, you can specify the menu program using the
executable name or full path and the args (flags and options) it should get
passed. If some argument contains the placeholder {prompt}, it is replaced
with a prompt such as "Switch to window" depending on context.
The format section
In the [format] section, format strings are specified defining how selection
choices are to be layed out. wofi supports pango
markup which makes it possible
to style the text using HTML and CSS. The following formats are supported
right now.
output_formatdefines how outputs (monitors) are displayed in the menu program,workspace_formatdefines how workspaces are displayed,container_formatdefines how non-workspace containers are displayed, andwindow_formatdefines how application windows are displayed.- In these formats, the following placeholders can be used:
{name}gets replaced by the output name, the workspace number or name or a window's title. The placeholder{title}is an obsolete synonym which will be removed in a later version.{layout}shows the workspace or container's layout.{id}gets replaced by the sway-internal con id.{indent}gets replaced with N times the newformat.indentvalue where N is the depth in the shown menu input.{app_name}gets replaced with a window's application name.{marks}shows a comma-separated list of the container's or window's marks.{app_icon}shows the application's icon (a path to a PNG or SVG file).{workspace_name}gets replaced with the name or number of the workspace the container or window belongs to.- The placeholders
{urgency_start}and{urgency_end}get replaced by the empty string if the window has no urgency flag and with the values of the same-named formats if the window has the urgency flag set. That makes it possible to highlight urgent windows as shown in the default config.
indentis a string which is repeatedly inserted at the{indent}placeholder in formats.html_escapedefines if the strings replacing the placeholders above (except for{urgency_start}and{urgency_end}) should be HTML-escaped.urgency_startis a string which replaces the{urgency_start}placeholder inwindow_format.urgency_endis a string which replaces the{urgency_end}placeholder inwindow_format.icon_dirsis a vector of directories in which to look for application icons in order to compute the{app_icon}replacement.fallback_iconis a path to some PNG/SVG icon which will be used as{app_icon}if no application-specific icon can be determined.
All the placeholders except {app_icon},
{indent}, {urgency_start}, and {urgency_end} may optionally provide a
format string as specified by Rust's
std::fmt. The syntax is
{<placeholder>:<fmt_str><clipped_str>}. For example, {app_name:{:>10.10}}
would mean that the application name is printed with exactly 10 characters. If
it's shorter, it will be right-aligned (the >) and padded with spaces, if
it's longer, it'll be cut after the 10th character. Another example,
{app_name:{:.10}...} would mean that the application name is truncated at 10
characters. If it's shorter, it will be printed as-is (no padding), if it's
longer, it'll be cut after the 10th character and the last 3 characters of that
substring will be replaced with ... (<clipped_str>).
It is crucial that during selection (using wofi or some other menu program)
each window has a different display string. Therefore, it is highly
recommended to include the {id} placeholder at least in container_format
and window_format. Otherwise, e.g., two vertical splits on the same
workspace or two terminals (of the same terminal app) with the same working
directory (and therefore, the same title) wouldn't be distinguishable.
Hint for wofi: wofi supports icons with the syntax
'img:<image-file>:text:<text>', so a suitable window_format with
application icon should start with img:{app_icon}:text:.
Hint for rofi: rofi supports icons with the syntax
"<text>\u0000icon\u00001f<image-file>", so a suitable window_format with
application icon should end with "\u0000icon\u001f<image-file>". Also note
that you must enclose your window_format value with double-quotes and not
with single-quotes. Singe-quote strings are literal strings in
TOML where no escape-sequences are
processed whereas for double-quoted strings (so-called basic strings)
escape-sequences are processed. rofi requires a null character and a
PARAGRAPH SEPARATOR for image sequences.
The layout section
In the [layout] section, you can enable auto-tiling by setting auto_tile to
true (the default is false). The option
auto_tile_min_window_width_per_output_width defines the minimum width in
pixels which your windows should have per output width. For example, the
example setting above says that on an output which is 1600 pixels wide, each
window should have at least a width of 780 pixels, thus there may be at most
two side-by-side windows (Caution, include your borders and gaps in your
calculation!). There will be no auto-tiling doesn't include your output's
exact width.
If auto_tile is enabled, swayr will automatically split either vertically or
horizontally according to this algorithm:
- For all outputs:
- For all (nested) containers on that output (except the scratchpad):
- For all child windows of that container:
- If the container is split horizontally and creating another window
would make the current child window smaller than the minimum width,
execute
split vertical(theswaymsgcommand over IPC) on the child. - Else if the container is split vertically and now there is enough space
so that creating another window would still leave the current child
window above or equal to the minimum width, call
split horizontalon the child. - Otherwise, do nothing for this container. This means that stacked or tabbed containers will never be affected by auto-tiling.
- If the container is split horizontally and creating another window
would make the current child window smaller than the minimum width,
execute
- For all child windows of that container:
- For all (nested) containers on that output (except the scratchpad):
There is one caveat: it would be nice to also trigger auto-tiling when windows or containers are resized but unfortunately, resizing doesn't issue any events over IPC. Therefore, auto-tiling is triggered by new-window events, close-events, move-events, floating-events, and also focus-events. The latter are a workaround and wouldn't be required if there were resize-events.
Version changes
Since version 0.8.0, I've started writing a NEWS file listing the
news, and changes to swayr commands or configuration options. If something
doesn't seem to work as expected after an update, please consult this file to
check if there has been some (possibly incompatible) change requiring an update
of your config.
Swayrbar
swayrbar is a status command for sway's swaybar implementing the
swaybar-procotol(7).
This means, you would setup your swaybar like so in your
~/.config/sway/config:
bar {
swaybar_command swaybar
# Use swayrbar as status command with some logging output which
# is redirected to /tmp/swayrbar.log. Be sure to only redirect
# stderr because the swaybar protocol requires the status_command
# to emit JSON to stdout which swaybar reads.
status_command env RUST_BACKTRACE=1 RUST_LOG=swayr=debug swayrbar 2> /tmp/swayrbar.log
position top
font pango:Iosevka 11
height 20
colors {
statusline #f8c500
background #33333390
}
}
swayrbar, like waybar, consists of a
set of modules which you can enable and configure via its config file, either
system-wide (/etc/xdg/swayrbar/config.toml) or per user
(~/.config/swayrbar/config.toml). Modules emit information which swaybar
then displays and mouse clicks on a module's space in swaybar are propagated
back and trigger some action (e.g., a shell command).
Right now, there are the following modules:
- The
windowmodule can show the title and application name of the current window in sway. - The
sysinfomodule can show things like CPU/memory utilization or system load. - The
batterymodule can show the current state of charge, the state (e.g., charging), and the state of health. - The
datemodule can show, you guess it, the current date and time! - The
pactlmodule can show the current volume percentage and muted state. Clicks can increase/decrease the volume or toggle the mute state.
I guess there will be more modules in the future as time permits. I personally
would enjoy a volume module. Patches are certainly
very welcome!
Screenshots
Installation
You'll need to install the current stable rust toolchain using the one-liner shown at the official rust installation page.
Then you can install swayrbar like so:
cargo install swayrbar
For getting updates easily, I recommend the cargo install-update plugin.
# Install it once.
cargo install install-update
# Then you can update all installed rust binary crates including swayr using:
cargo install-update --all
# If you only want to update swayr, you can do so using:
cargo install-update -- swayrbar
Configuration
When swayrbar is run for the very first time and doesn't find an existing
configuration file at ~/.config/swayrbar/config.toml (user-specific) or
/etc/xdg/swayrbar/config.toml (system-wide), it'll create a new user-specific
one where all modules are enabled and set up with some reasonable (according to
the author) default values. Adapt it to your needs.
The syntax of the config file is TOML. Here's a short example with all top-level options (one!) and one module.
refresh_interval = 1000
[[modules]]
name = 'window'
instance = '0'
format = '🪟 {title} — {app_name}'
html_escape = false
[modules.on_click]
Left = ['swayr', 'switch-to-urgent-or-lru-window']
Right = ['kill', '{pid}']
The refresh_interval defines the number of milliseconds between refreshes of
swaybar.
The remainder of the configuration defines a list of modules with their
configuration (which is an array of
tables in TOML where a module's
on_click).
nameis the name or type of the module, e.g.,window,sysinfo,battery,date,...instanceis an arbitrary string used for distinguishing two modules of the samename. For example, you might want to have twosysinfomodules, one for CPU and one for memory utilization, simply to have a separator between these different kinds of information. That's easily doable, just give them differentinstancevalues.formatis the string to be printed inswaybarwhere certain placeholders are substituted with module-specific values. Usually, such placeholders are written like{title}, i.e., inside braces. Like inswayr, formatting (padding, aligning, precision, etc.) is available, see here.html_escapedefines if<,>, and&should be escaped as<,>, and&becauseformatmay contain pango markup. Obviously, if you make use of this feature, you want to sethtml_escape = truefor that module. This option is optional and may be omitted.on_clickis a table defining actions to be performed when you click on a module's space inswaybar. All placeholders available informatare available here, too. The action for each mouse button is specified as an array['command', 'arg1', 'arg2',...]. The available button names to be assigned to areLeft,Middle,Right,WheelUp,WheelDown,WheelLeft, andWheelRight.
The on_click table can also be written as inline table
on_click = { Left = ['swayr', 'switch-to-urgent-or-lru-window'], Right = ['kill', '{pid}'] }
but then it has to be on one single line.
The window module
The window module supports the following placeholders:
{title}or{name}expand to the currently focused window's title.{app_name}is the application name.{pid}is the process id.
By default, it has the following click bindings:
Leftexecutesswayr switch-to-urgent-or-lru-window.Rightkills the process of the window.
The sysinfo module
The sysinfo module supports the following placeholders:
{cpu_usage}is the percentage of CPU utilization.{mem_usage}is the percentage of memory utilization.{load_avg_1}is the average system load in the last minute.{load_avg_5}is the average system load in the last five minutes.{load_avg_15}is the average system load in the last fifteen minutes.
By default, it has the following click bindings:
Leftexecutesfoot htop.
The battery module
The battery module supports the following placeholders:
{state_of_charge}is the percentage of charge wrt. the battery's current capacity.{state_of_health}is the percentage of the battery's remaining capacity compared to its original capacity.{state}is the current state, e.g., something like Discharging or Full.
The pactl module
The pactl module requires the pulse-audio command line tool of the same name
to be installed. It supports the following placeholders:
{volume}is the current volume percentage of the default sink.{muted}is the string" muted"if the default sink is currently muted, otherwise it is the empty string.
By default, it has the following click bindings:
Leftcalls thepavucontrolprogram (PulseAudio GUI control).Righttoggles the default sink's mute state.WheelUpandWheelDownincrease/decrease the volume of the default sink.
The date module
The date module shows the date and time by defining the format using
chrono's strftime
format.
Questions & Patches
For asking questions, sending feedback, or patches, refer to my public inbox
(mailinglist). Please mention the
project you are referring to in the subject, e.g., swayr or swayrbar (or
other projects in different repositories).
Bugs
It compiles, therefore there are no bugs. Oh well, if you still found one or want to request a feature, you can do so here.
Build status
License
Swayr & Swarybar are licensed under the GPLv3 (or later).